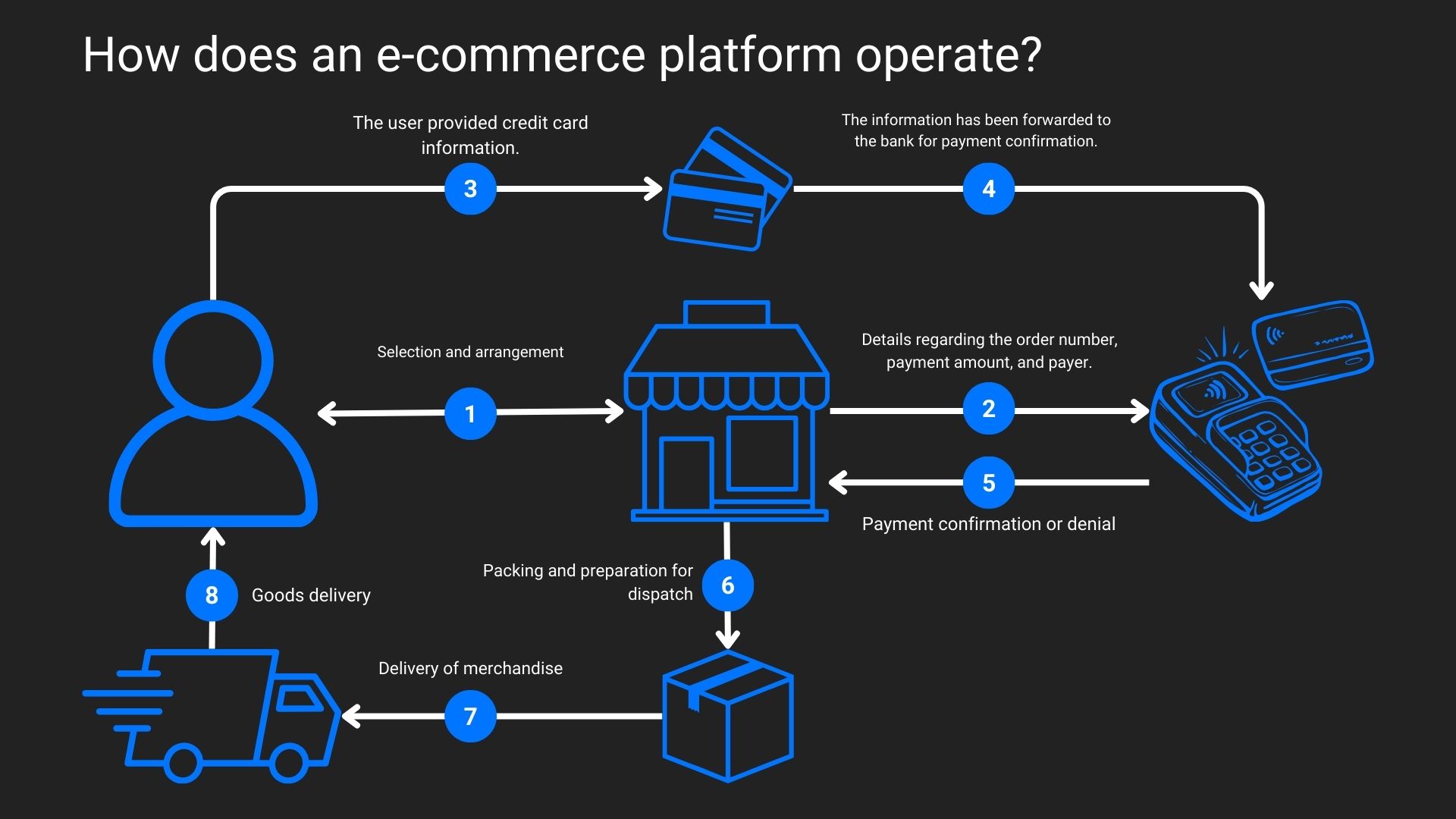
1.The user can select products and add them to the cart. First, the visitor enters the product catalog, familiarizing themselves with the assortment. The ergonomics of the catalog, proper navigation, and filter system are very important. This simplifies interaction with the site.
After the products are selected, they can add them to the cart and continue searching for other items. In the cart, the customer can edit the quantity of items, add/remove products.
2.Once the customer has chosen everything they were looking for and added it to the cart, they can begin the checkout process. If the buyer already has a profile on the site, they do not need to enter the information, as it will be filled in automatically. The client only checks its relevance.
If there is no profile, the client is presented with a form that is important to fill out. The form requires the following data:
- personal data;
- phone number;
- payment method (from credit card to cash on delivery);
- enter a promo code, if available;
- choose an appropriate delivery method;
- select a post office or courier delivery.
3.After filling out the form, the client goes to the payment page for the product. There, they can double-check all the information, select a payment system, and make the payment. Among the most popular methods will be:
- debit/credit cards Visa;
- debit/credit cards MasterCard;
- PayPal;
- Apple Pay;
- Google Pay.
Payment methods may differ depending on the buyer's GEO.
4.Then the order processing and confirmation begin. After the payment is completed, the user receives a notification that the order is being processed. When all the data has been verified, the user will receive a notification that the order is confirmed and ready for shipment. In some stores, users can track the status of their order in real-time.
5.The delivery phase begins. The order is handed over to the post office and sent to the buyer.
6.After the client receives the order, they need to be encouraged to provide feedback. Questions or complaints from customers cannot be ignored. The store's task is to do everything to ensure that the customer makes a purchase, is satisfied, and returns again. It is important to assist the customer with product returns, exchanges, respond to their questions, and provide support if there are issues with the order.
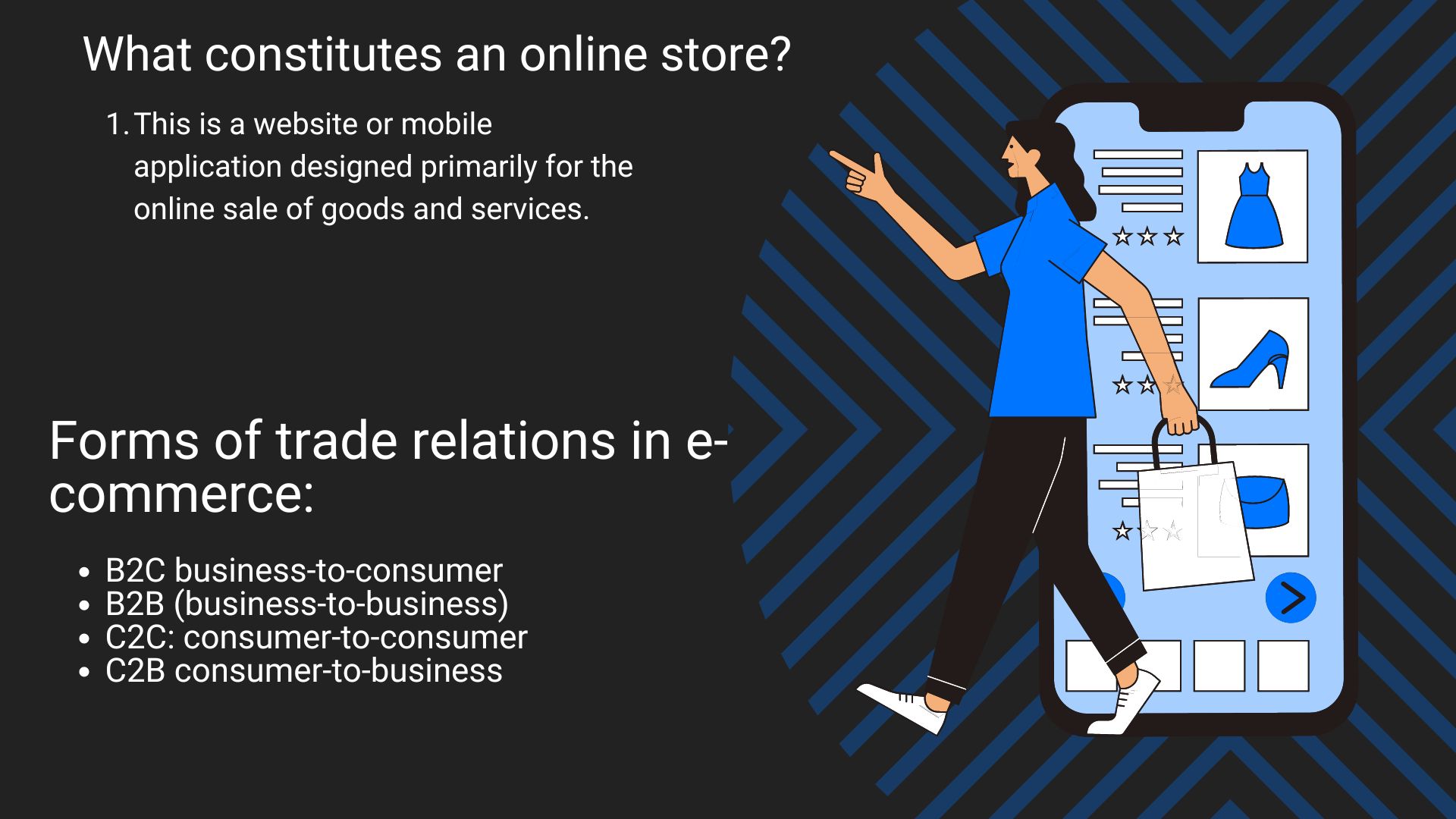
Main elements of the online store
We have already figured out what an online store is, and now let’s go through its structure. You should have a rough idea of what to expect from the future project.
Frontend
This part of your store will interact with the customer. The frontend consists of:
- design;
- interface;
- catalog structure;
- product cards.
The frontend is responsible for the usability of your site. HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are used to create the frontend.
Backend
This part of the site is not visible to the client and does not interact with it. The backend is responsible for:
- the logic of the online store;
- data management;
- data processing;
- interaction with databases;
- order management;
- payments, and so on.
To implement all these functions, the following technology stack is used: server-side programming languages (Python, Ruby, PHP), database management systems (MySQL or PostgreSQL).
Product catalog
The product catalog has been, is, and will be the foundation of the online store. It displays all the product positions that your store can offer to the buyer. Special attention should be paid to creating the catalog, as the ergonomics and quality of the catalog affect the customer experience. A good product catalog contains:
- product names;
- product categories;
- filter system;
- detailed product descriptions;
- technical/quality characteristics of the products;
- high-quality, unique product photos;
- video reviews;
- system for customer reviews and comments.
Shopping cart
The cart allows customers to collect products without interrupting the payment process. This is convenient and allows the user to spend more time browsing the catalogs. This improves customer retention metrics on the site.
Payment system or payment gateways
The payment system for products should be convenient and flexible. Moreover, it should be adapted to different GEOs. Each country has its popular methods of paying for goods. If, in most European countries, it will be bank cards, in the USA, it will be PayPal, while in Asia, there are other services. This aspect needs to be considered at the stage of integrating payment gateways.
Having a variety of payment options not only demonstrates your customer orientation but also increases the chances of making a purchase, enhancing audience loyalty.
Order delivery system
The same applies to the payment system. Each country and region has its preferred delivery services. Somewhere it will be DHL, FedEx, while in other places, it may be UPS or Royal Mail.
The delivery system should be flexible and diverse. Consider integrating with services in advance to ensure a positive shopping experience for customers.
Content Management System (CMS)
The CMS allows you to manage the content within the store. With it, you can:
- add new products to the catalogs;
- update information in product cards;
- publish news;
- create blogs;
- add guides and instructions.
Which one to choose? It all depends on a number of factors, including the scale of your business. But here are some of the most popular CMS options: Magento, WooCommerce, Shopify. These systems are popular, have proven themselves well, and offer great potential for scaling and personalizing the store. This is all thanks to the modular system and separate stores with plugins and extensions.
Advantages of online stores